Tutorial: CLI
This tutorial outlines how to create a simple command-line interface with Noderize. You can see the final code here.
Our goal is to:
- Have a default help command
- Have 2 sub-commands:
greet: Asks for your name and says hellofibonacci: Generate numbers in the fibonacci series
We will be using 3 libraries:
Commander.js: Commands and sub-commandschalk: Color our outputInquirer.js: Prompts
Time required: ~10 minutes.
Setup
To start, create your Noderize app and cd into it:
yarn create noderize basic-cli
# or
npx create-noderize basic-cli
# then
cd basic-cli
Next, we'll install our dependencies:
yarn add commander chalk inquirer
# or
npm install commander chalk inquirer
Our package.json should look something like this (except the versions being the latest):
{
"name": "basic-cli",
"version": "0.1.0",
"private": true,
"scripts": {
"watch": "noderize-scripts watch",
"test": "noderize-scripts test",
"format": "noderize-scripts format",
"build": "noderize-scripts build",
"start": "noderize-scripts start"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@noderize/scripts": "*"
},
"dependencies": {
"@noderize/runtime": "*",
"chalk": "^2.3.0",
"commander": "^2.14.1",
"inquirer": "^5.1.0"
}
}
Structure
We will have 3 files under src:
index.js: The entry point, handles commands and dispatches sub-commandsgreet.js: Thegreetsub-command handlerfibonacci.js: Thefibonaccisub-command handler
Let's clear index.js and create the other files:
rm src/index.js
touch src/index.js src/greet.js src/fibonacci.js
In our greet.js and fibonacci.js, we'll make them export a single function that runs the sub-command. We'll pre-emptively import them with our other dependencies:
import program from "commander";
import chalk from "chalk";
import greet from "./greet";
import fibonacci from "./fibonacci";
Next, we'll define our commands. We'll define greet with optional name argument and fibonacci with optional n argument, and route them to their respective imported commands:
program.command("greet [name]").action(greet);
program.command("fibonacci [n]").action(fibonacci);
Next, we'll add a catch-all command (if entering a non-valid command). We will firstly show a message to the user, then show them the general help message, and exit with error code 1.
program.action(() => {
console.log(chalk.yellowBright("\n Command not found"));
program.outputHelp();
process.exit(1);
});
Finally, we'll make Commander run by passing our program's arguments to it, and we will show the general help if no command is passed:
program.parse(process.argv);
if (!process.argv.slice(2).length) {
program.outputHelp();
}
Greet
We'll first implement the greet command. First, we'll import our dependencies and make it export an async function that accepts our argument, name:
import inquirer from "inquirer";
import chalk from "chalk";
export default async name => {
// Code here
};
In the function, we'll ask the user for a name if they did not pass it as an argument:
if (name === undefined) {
const answers = await inquirer.prompt([
{ name: "name", message: "What is your name?" }
]);
name = answers.name;
}
Next, we'll greet the user with color:
console.log(`Hello ${chalk.blueBright(name)}!`);
Fibonacci
In our Fibonacci, we'll also ask the user for a n if it doesn't exist, but we will add a validator to check if the prompt is a number:
import inquirer from "inquirer";
import chalk from "chalk";
export default async n => {
if (n === undefined) {
const answers = await inquirer.prompt([
{
name: "n",
message: "N?",
validate(value) {
if (/^\d+$/.test(value)) {
// Is a number
return true;
} else {
// Error message
return "Value is not a positive integer.";
}
}
}
]);
n = answers.n;
}
// Code here
};
Next, we'll convert our string value to a number, and error if it is not valid:
n = parseInt(n);
if (isNaN(n) || n < 1) {
console.log(chalk.yellowBright("Value of n is not a positive integer."));
process.exit(1);
}
For our fibonacci command, we will steal borrow from a great article. We're going to add this at the bottom of the file, out of the function.
function fibonacci(num, memo = {}) {
if (memo[num]) return memo[num];
if (num <= 1) return 1;
return (memo[num] = fibonacci(num - 1, memo) + fibonacci(num - 2, memo));
}
To finish off this sub-command, we'll calculate the value and display it to the user (inside our main function):
const value = fibonacci(n);
console.log(
`Fibonacci for n=${chalk.blueBright(n)} = ${chalk.blueBright(value)}!`
);
Running
Now that we are done our commands, let's build our app:
yarn build
# or
npm run build
We can now run it with arguments using the start script (or Node) like so:
yarn start greet
# or
npm start fibonacci
# or
node dist/index.js --help
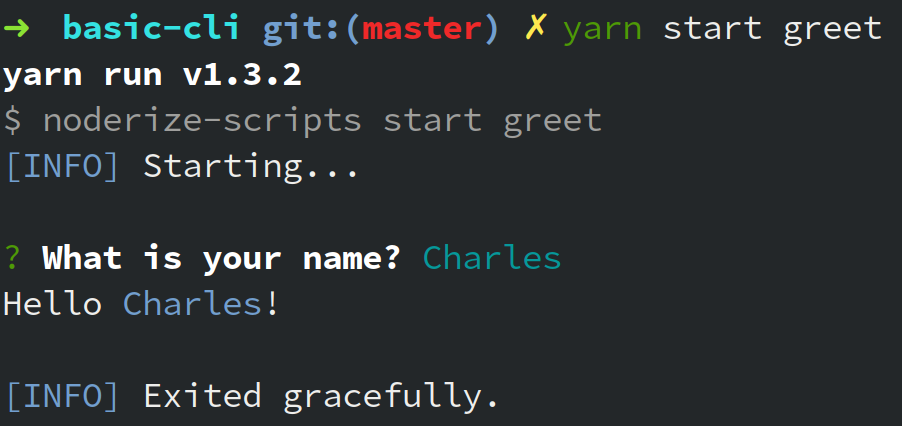
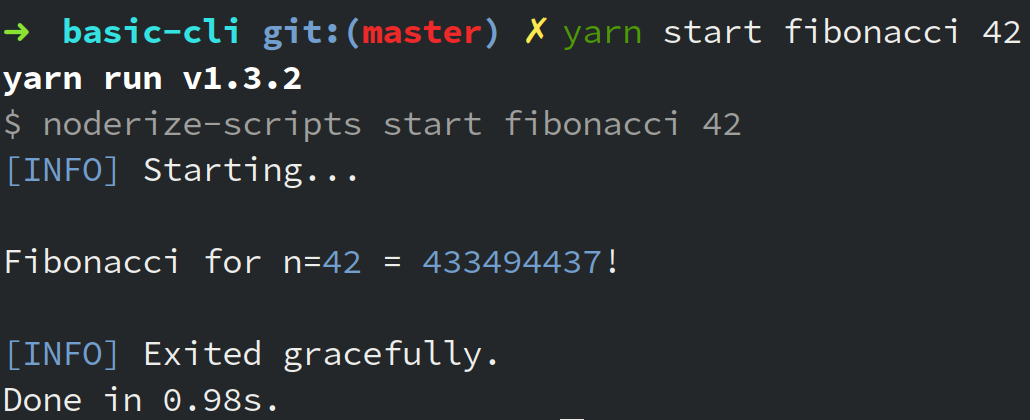
Finished!
Summary
In this tutorial we saw how to: